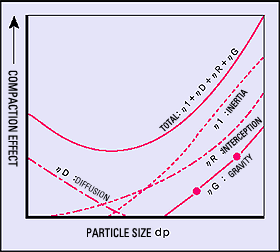
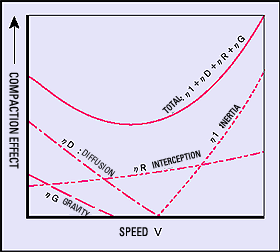
| Since the air filter is a fiber layer with high space efficiency, it is compacted in the following 4 effects from 1 fiber strand within the filter. |
| |
|
 |
1) Inertia
The particle approaching the fiber from airflow collides on the fiber by self inertia beyond from air current. As the filtration speed gets larger, the effect appears. |
| |
2) Brownian Diffusion
A small particle shows the Brownian diffusion movement regardless of the airflow. Hence, even the large particle that passes through the filter fiber along with the air current is also compacted on the fiber since the movement distance is long and it has no direction. The effect becomes larger if the particle filtration speed is slower. |
| |
3) Interception
Although the particle moves along with the airflow, it collides with the fiber and is compacted since a particle has a size. This effect occurs when the particle and fiber size ratio is larger. |
| |
4) Gravitational Settling
Due to its own gravity that approaches to the fiber from the airflow, particle exits from the air current and is settled and compacted. This effect occurs when the particle size is large and the filtration speed is slow. |
| |
|
 |
| Although the particles overlapped with these effects are compacted on the filter fiber, the change by the respective effective particle size and speed may be shown in the lower left diagram. The actual filter compaction efficiency has the trend in the lower right diagram. |
| |
 |
 |
|
| |
|



